What is Rh incompatibility?
Rh incompatibility occurs during pregnancy if
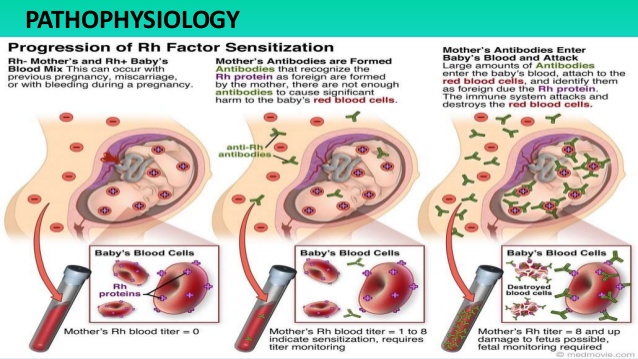
There are four big blood types: B, A, O, and AB. The kinds are based on materials on the surface of the blood cells. Another blood form is named Rh. Human blood type inherits Rh factor type from their parents. A small percentage of Individuals are Rh-negative, although most Individuals are Rh-positive. This means they lack the Rh protein.
Your body will produce antibodies (proteins) against the baby’s Rh-positive blood. These antibodies usually don’t cause problems during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the baby is born before lots of the antibodies grow.
When they’ve formed, however, the antibodies stay in your body. Thus, Rh incompatibility is far more likely to cause difficulties in second or later pregnancies (if the infant is Rh-positive).
When the Rh antibodies cross the placenta it may attack the baby’s red blood cells.
Hemolytic anemia is a condition where blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be replaced by the body. Oxygen is carried by red blood cells across all regions of the body.
Without enough red blood cells, then your baby will not get enough oxygen. This may lead to serious issues. Severe hemolytic anemia may be deadly to your child.
Overview of Rh Incompability
With proper and prompt healthcare and screening, you can prevent the problems of Rh. Screening tests allow your doctor to find out early in your pregnancy whether you’re at risk for the condition.
If you’re at risk, your physician will carefully check on you and your
A medicine injection called Rh immune globulin can prevent your body from making Rh antibodies. This medicine helps prevent Rh incompatibility problems. If you are Rh-negative, then you will need this medication every single time you have a baby with blood.
Other events also can expose you. Examples include a miscarriage or blood transfusion. If you’re treated with Rh immune globulin shortly after those events Might be able to avoid Rh incompatibility.
Risk Factors of Rh Incompatibility
An Rh-negative woman who conceives a child with an Rh-positive man is at risk for Rh. If you’re Rh-negative, your risk of problems from Rh incompatibility is greater if you were exposed to blood that is Rh-positive prior to the pregnancy. This Might have occurred during
An earlier pregnancy (usually during delivery). You might also have been subjected to Rh-positive blood if you’d bleeding or abdominal injury (for example, from a car accident) during the pregnancy. (An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that begins out of the uterus, or uterus ) An injection or puncture with a needle or other item comprising Rh-positive blood. Straightforward blood tests can reveal whether you and the father of your baby are Rh-positive or Rh-negative
Particular tests can show you Rh-positive blood. Examples include amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Amniocentesis is a test that you may have throughout pregnancy. Your doctor uses a needle to remove a little bit of fluid in the sac around your infant. The fluid is tested for various factors.
CVS also may be performed during pregnancy. With this evaluation, your doctor threads a thin tube through the vagina and cervix to the placenta. The doctor removes a tissue sample from the placenta with the help of gentle suction. The tissue sample is analyzed for various reasons.
Unless you’re treated with the medicine that prevents Rh antibodies (Rh immune globulin) after every one of these occasions, you are at risk for Rh incompatibility throughout current and future pregnancies.
Treatment for Rh Incompatibility
Rh Incompatibility can be avoided using Rh immune globulin. The medication will assist As soon as you’ve shaped Rh antibodies.
Thus, a girl Has blood has to be treated with Rh immune globulin during and following or following any occasion which enables her blood.
Prenatal care can help
Your pregnancy can be carefully monitored by your physician if you are in danger. He or she’ll watch for signals of hemolytic anemia on your infant and provided treatment as necessary.
Signs, Symptoms, and Complications of Rh Incompatibility
Rh incompatibility doesn’t cause symptoms or signs in a woman who is pregnant. In a baby, the condition can lead to hemolytic anemia. Hemolytic anemia is a condition in which blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be replaced by the body.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin (HEE-muh-glow-bin), an iron-rich protein that carries oxygen to your system.
Anemia may cause signs and symptoms in a newborn, like jaundice and a buildup of fluid.
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin and whites of their eyes. When red blood cells die, they release hemoglobin to the bloodstream. The hemoglobin is broken down into a chemical. This chemical gives eyes and skin color. High levels of bilirubin may lead to brain damage in the infant.
The accumulation of fluid is a consequence of heart failure. Without red blood cells, the baby’s heart must work harder to move oxygen-rich blood. This stress can lead to heart failure.
Heart failure may cause fluid to accumulate in many regions of the human body. While this happens in a fetus or newborn, the condition is called hydrops fetalis (HI-drops fe-TAL-is).
Severe anemia may be deadly to your toddler at the time of birth or shortly after.